
Introduction - Theoritical preliminary study - Simulation under Simulink

Introduction - Theoritical
preliminary study - Simulation under Simulink
Download (french + english) : recepteur.zip (189ko)
| Introduction |
The system of FSK broadcasting covers, in France, the waveband [88MHz,108MHz]. The bandwidth B of the modulated signal vary between 200kHz and 250kHz and the signal’s bandwidth is b=15kHz ; it corresponds to human voice’s spectrum.
In this project, we’re going to try to demodulate such signals. So we want to realise a system that allows reception of a great number of messages m1(t), …,m2(t) (stations) modulated to carrier frequencies of different values, spaced of a constant quantity D(f). The system of reception covers a waveband B.
Introduction - Theoritical
preliminary study - Simulation under Simulink
| Theoretical
preliminary study |
The block diagram presented in figure 1 represents the classic reception system of a message mk(t) of bandwidth bk modulated to a frequency fk.

Figure 1 System of reception
To receive several messages, it
would be theoretically necessary that the receiver contains so
much demodulators that different carrier frequencies. It’s
easy to conceive this solution is very quickly impracticable as
soon as the number of stations is important. To solve this
difficulty, there exists a technique which instead of adapting
the demodulator to the frequency of the signal to modulate,
adapts the signal to a demodulator permanent. This operation is
allowed by returning all signals to receive, around a permanent
frequency, told intermediate frequency. This technique allows
therefore to use the same circuit of demodulation. It is the
heterodyne receiver.
In a first time we study messages on the canal of transmission
having undergone a modulation of amplitude without carrier
frequency. Results will be transposed to the FSK modulation by
the way.
Expression of the modulated signal: ![]() The spectrum density in power of the signal is then :
The spectrum density in power of the signal is then :  After the local oscillator, the spectrum density contain four
different parts : figure2 ; we need a bandpass filter to obtain a
modulated signal of permanent frequency fi : figure 3.
After the local oscillator, the spectrum density contain four
different parts : figure2 ; we need a bandpass filter to obtain a
modulated signal of permanent frequency fi : figure 3.

Figure 2
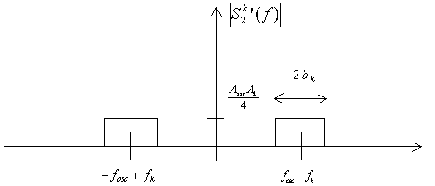
Figure 3
Signal enters then in the demodulator. This demodulator is
conceived to function to the intermediate frequency fI.
We choose fI = fosc- fk to
demodulate the signal modulated to the frequency fk.
Indeed after the local oscillator the spectrum of the signal is
around frequencies fosc - fk and fosc
+ fk.
When a signal is received around the carrier frequency f1
we just put fosc such sort that fosc - f1=fI.
Note : If fI is badly chosen fosc -
fk can be in the waveband [fosc - fk ,
fosc + fk] and therefore there can be
interferences with one other station.
We will take fI in the middle of the waveband
[88MHz,108MHz].
If we make a synchronous and coherent demodulation of the signal
s3(t), we obtains in exit of the receiver the signal 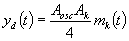 by
using for the filter 4 a lowpass filter.
by
using for the filter 4 a lowpass filter.
The interest of a such system of reception is with a demodulator
only, it is possible to receive messages modulated to different
carrier frequencies. You only need to vary fosc (a
potentiometer would allow to realise this operation).
Introduction - Theoritical
preliminary study - Simulation under Simulink
| Simulation under
Simulink |
We used here, modulators and demodulators in transposed band of
the communication toolbox of Simulink. All elements are typical
digital because in the next part we will use an acquisition card
that contains an analogue-digital converter. We will be therefore
brought to work on digital signals.

Figure 4
The figure 4 shows the model we realised under Simulink to
simulate an heterodyne receptor.
For the simulation we used values of sampling and modulation
frequency weaker than those used in practice. We have undertaken
the simulation by using a sinusoidal source. Moreover, to
facilitate the visualisation, we took a modulation frequency
relatively weak (close to the bandwidth of the signal). Thus we
can observe on the same graph the source, the result of the
modulation and the demodulated signal :

Figure 5
On the figure 5, we can notice that the signal at the exit of the
system corresponds to the initial signal with a small delay time
to the time of reply of the demodulator.